










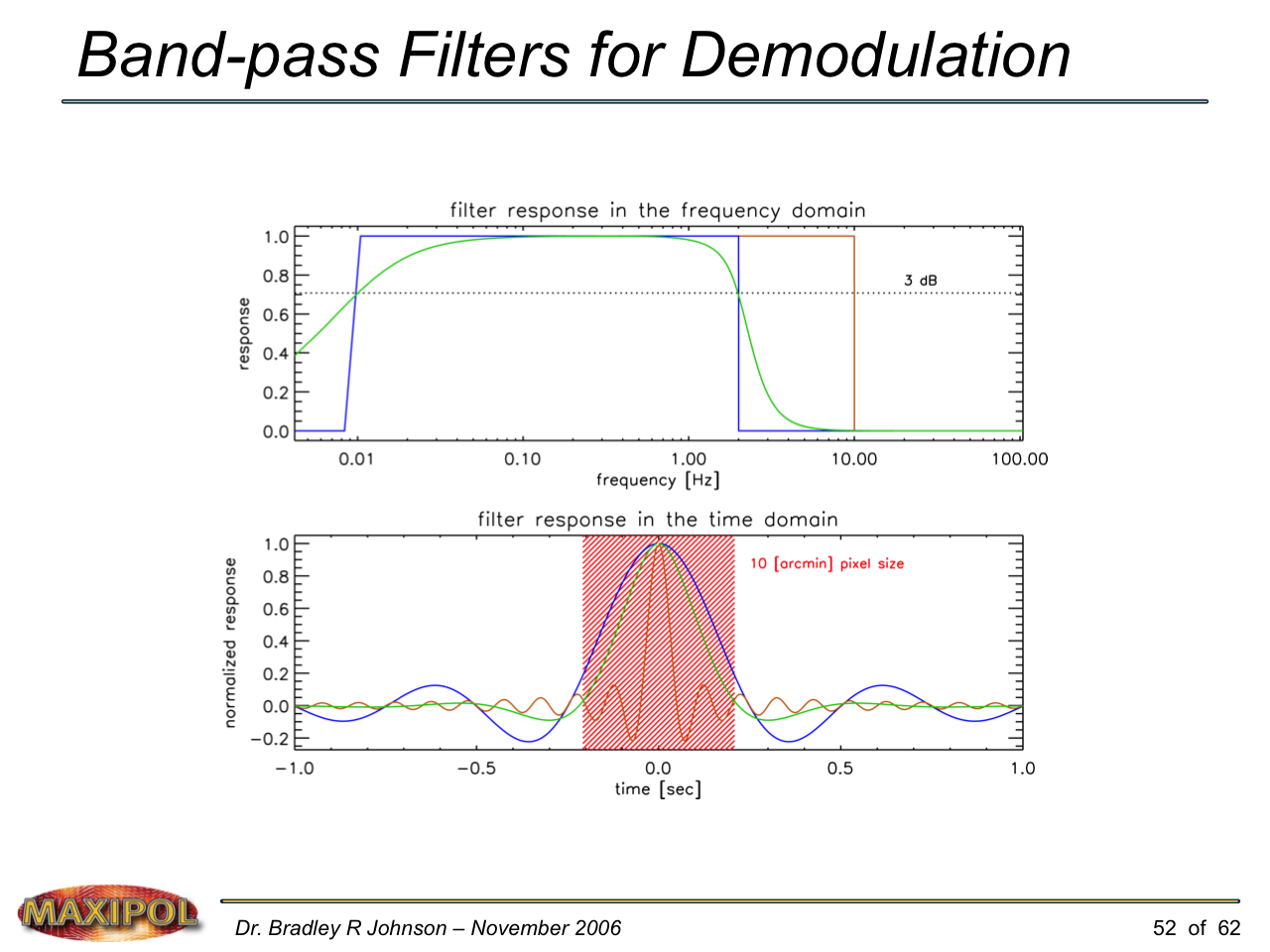
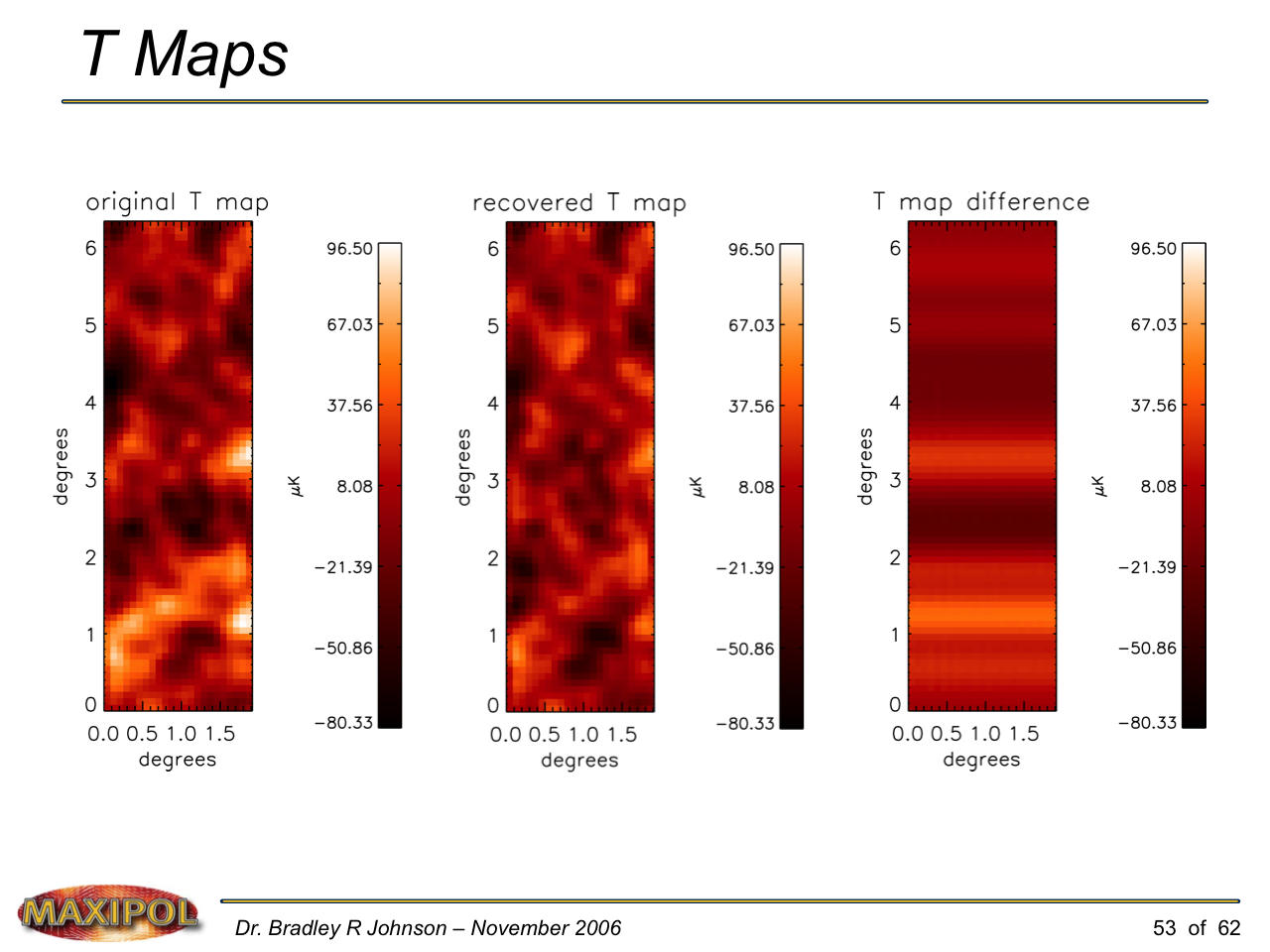
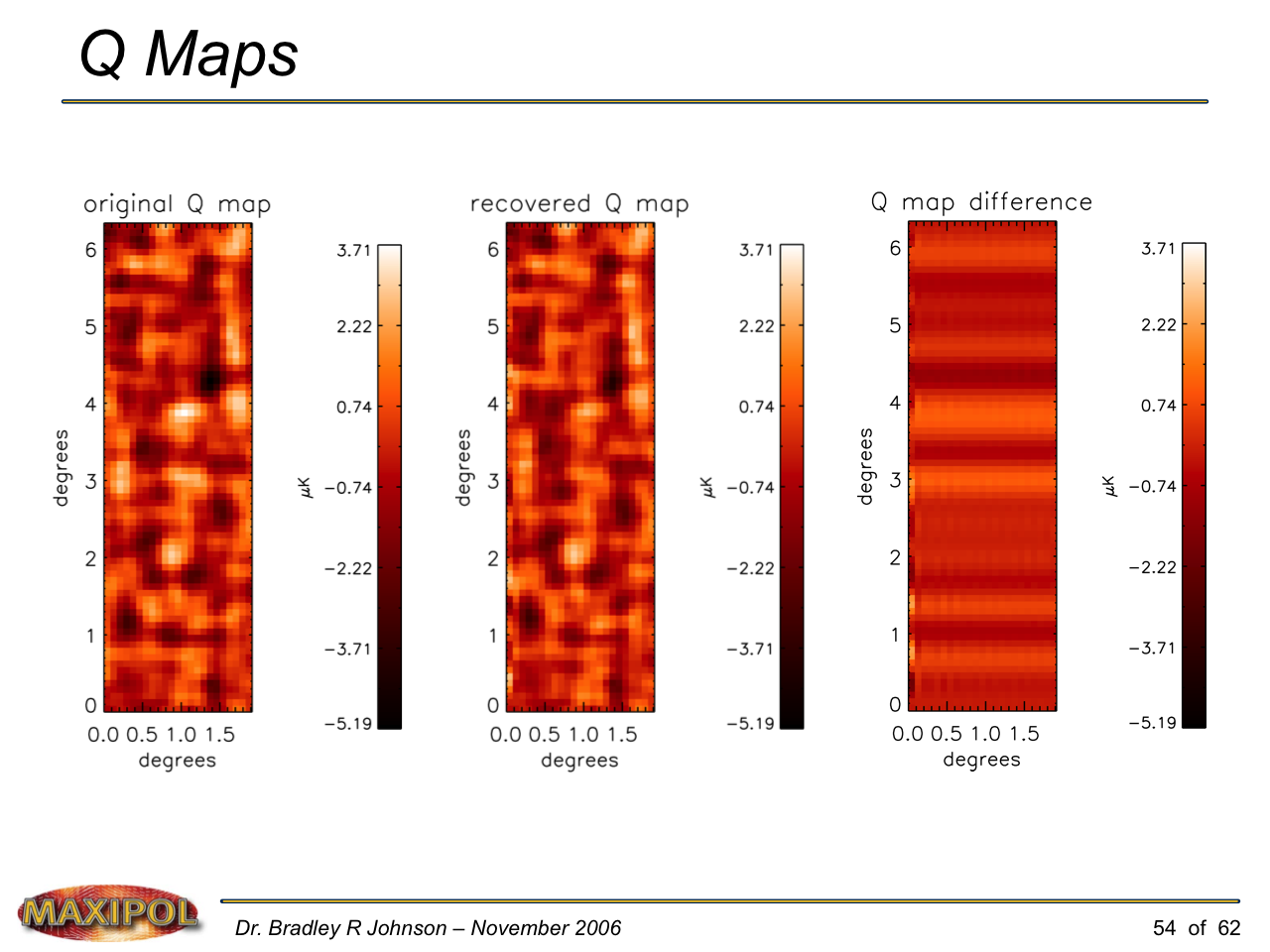
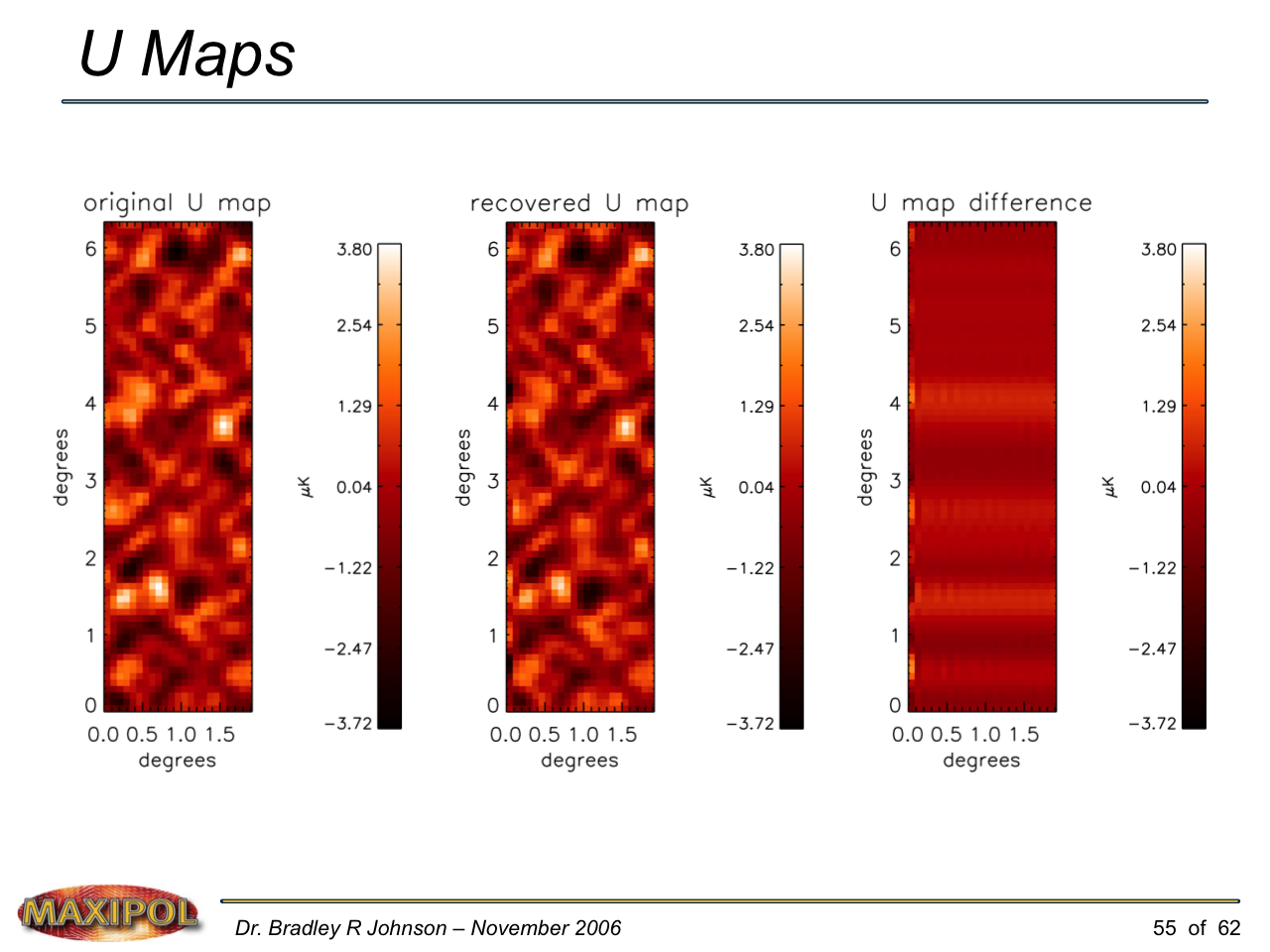

MAXIPOL
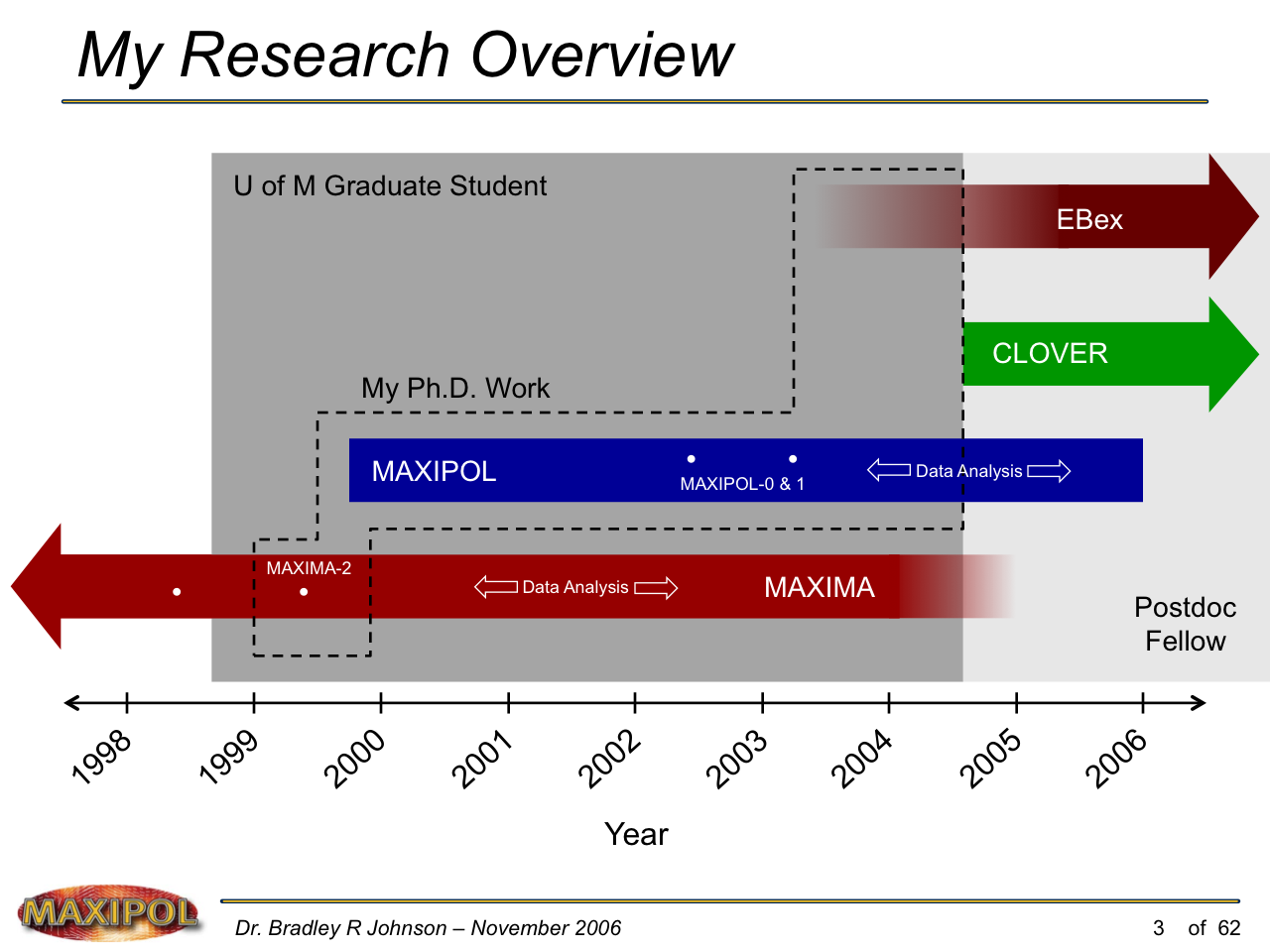
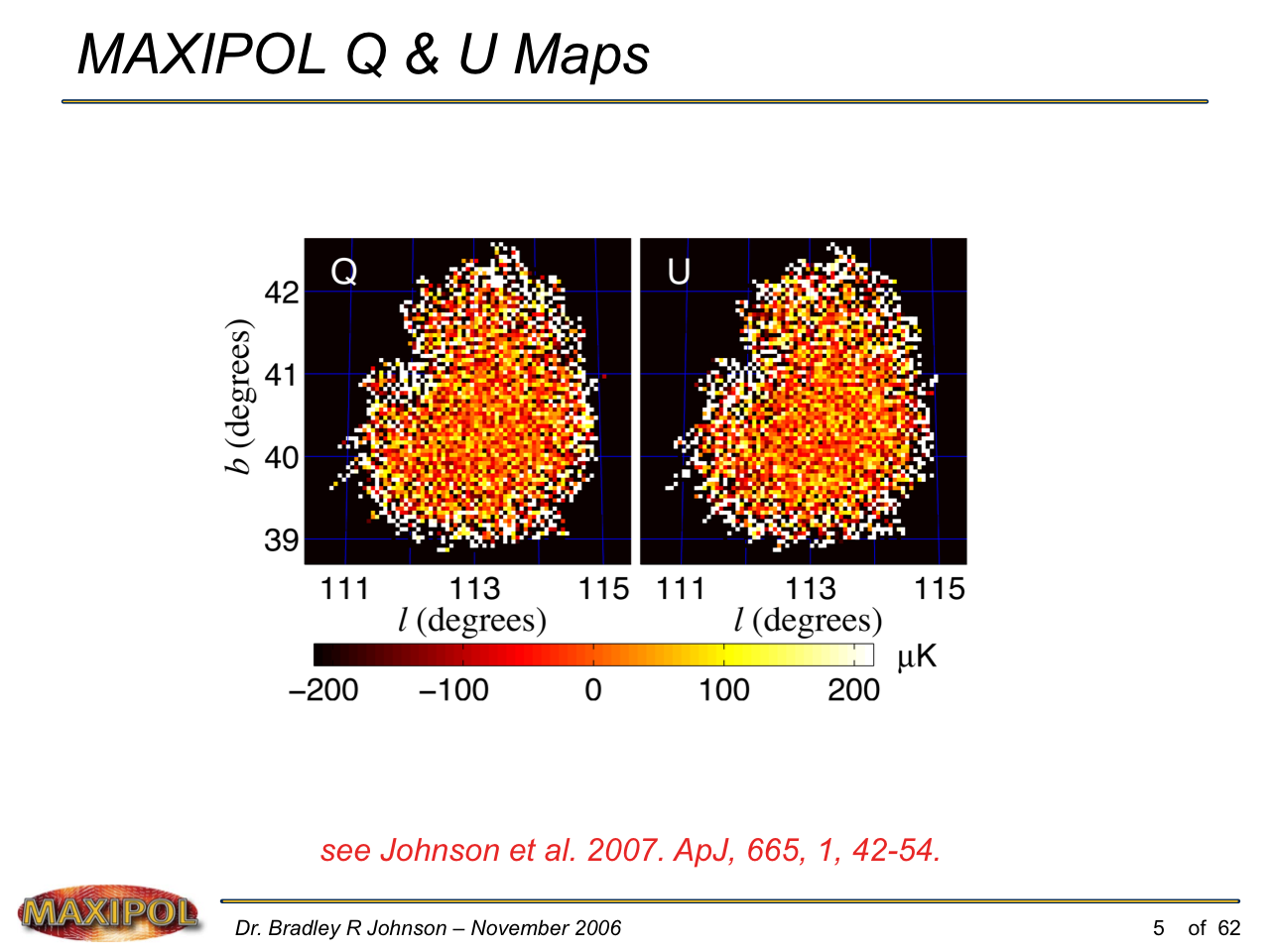
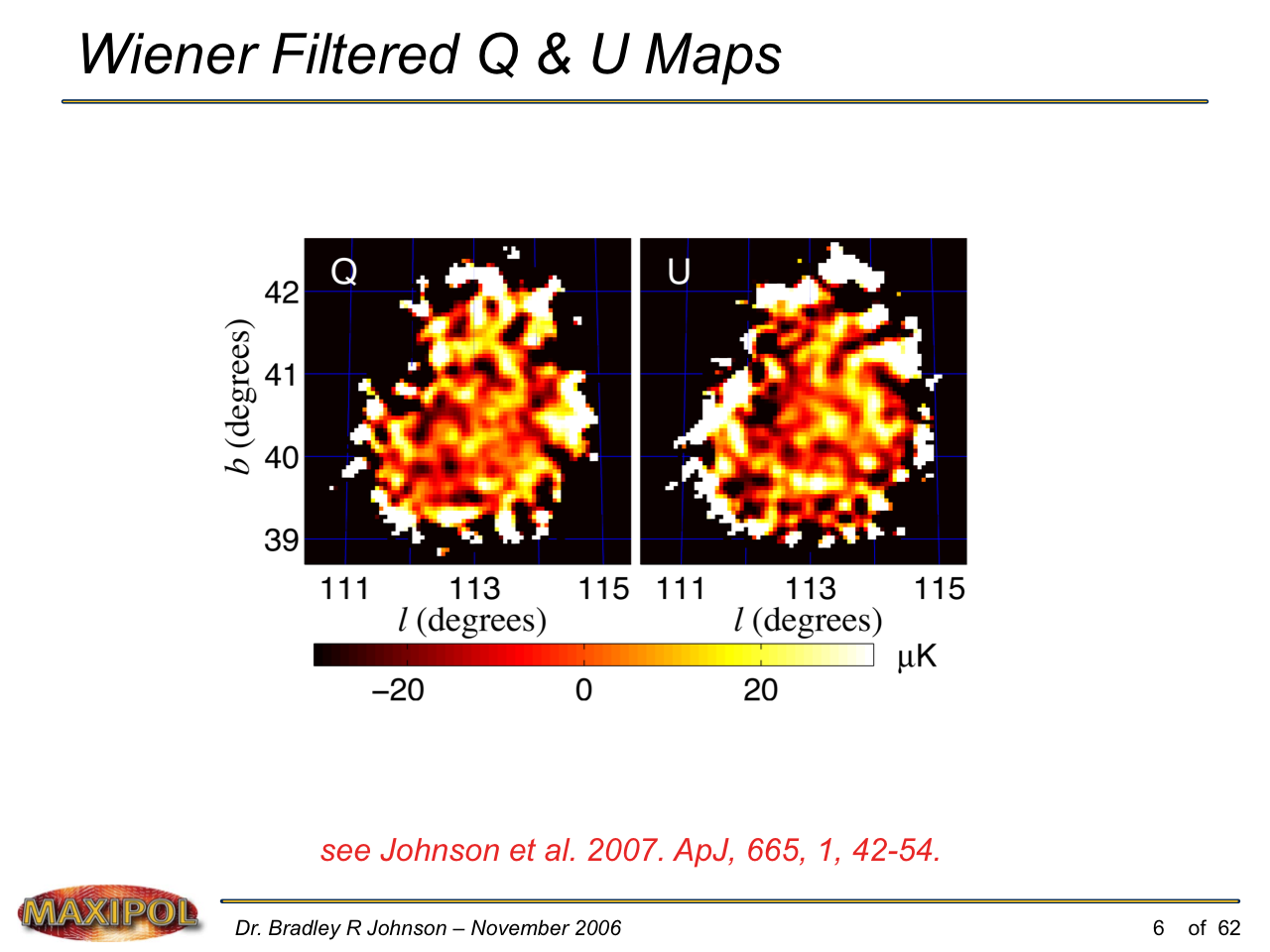
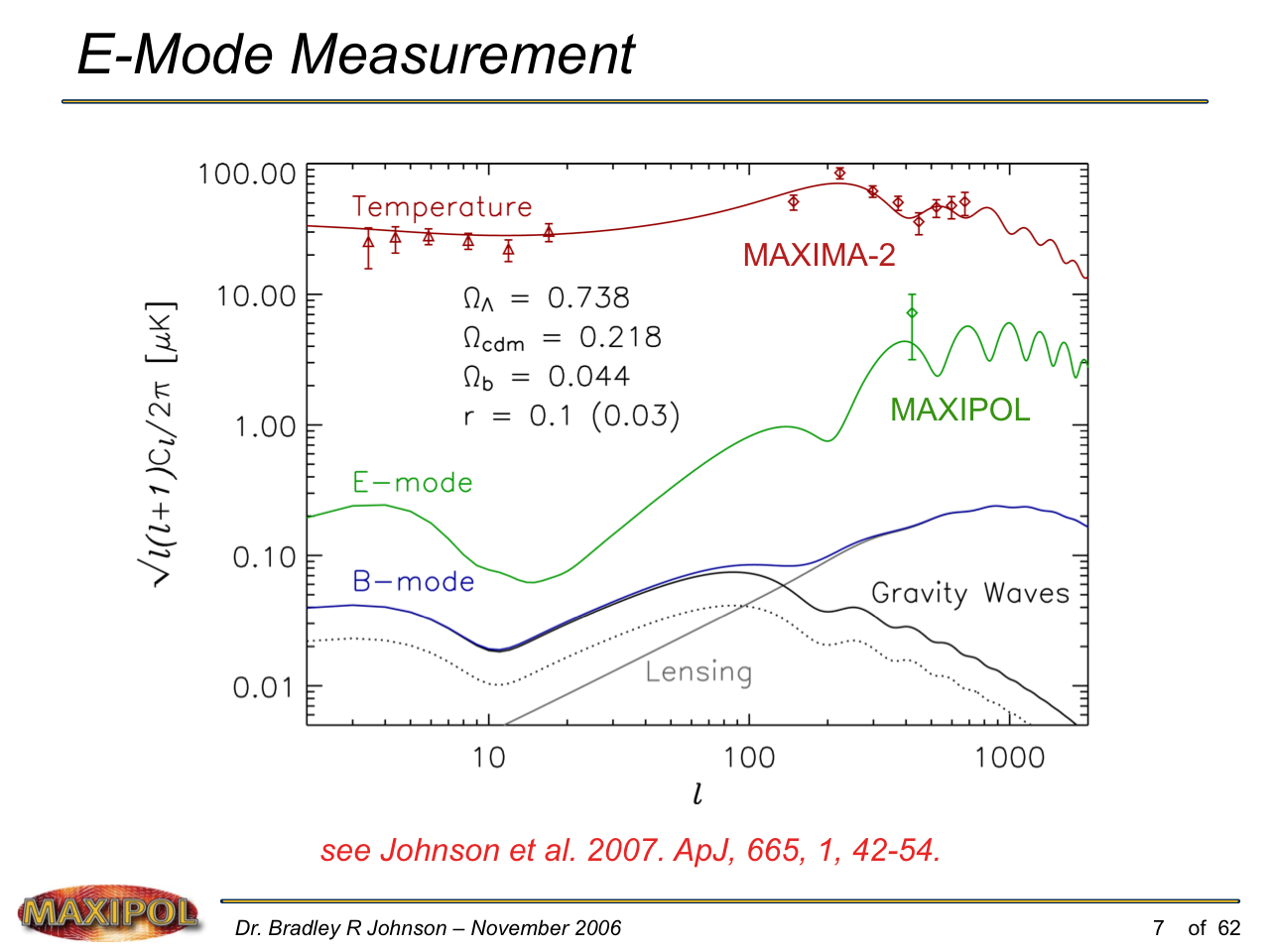
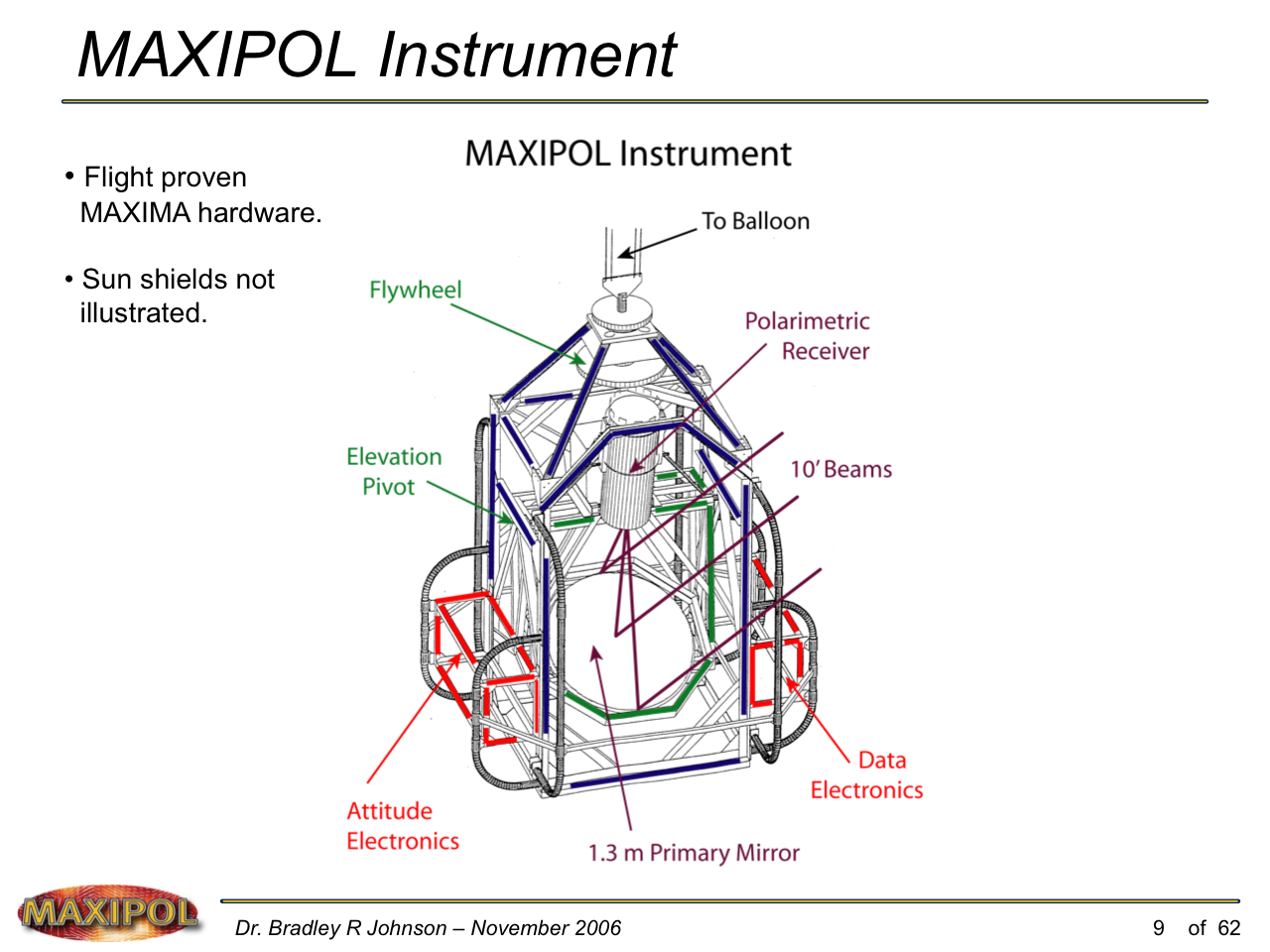
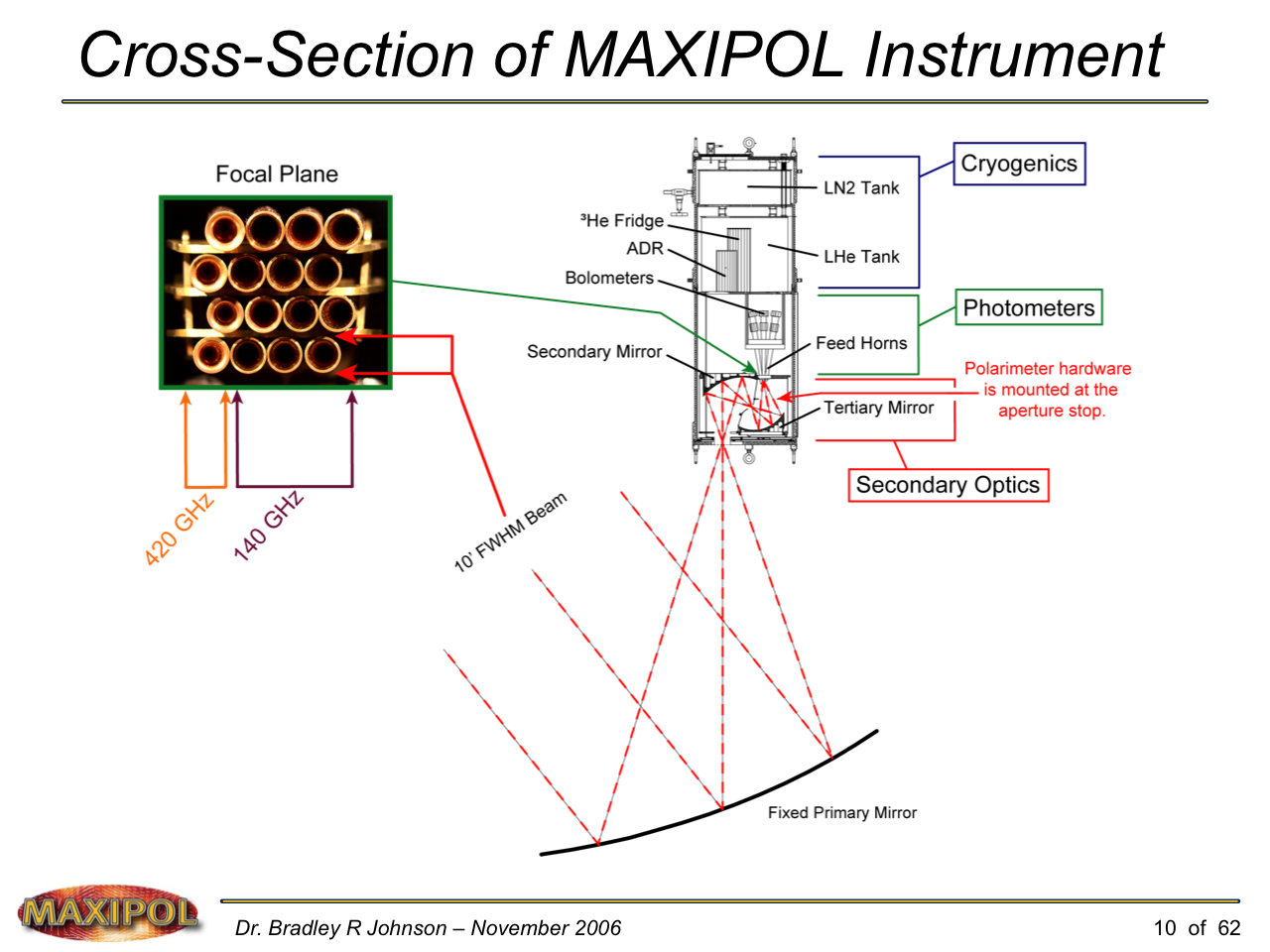
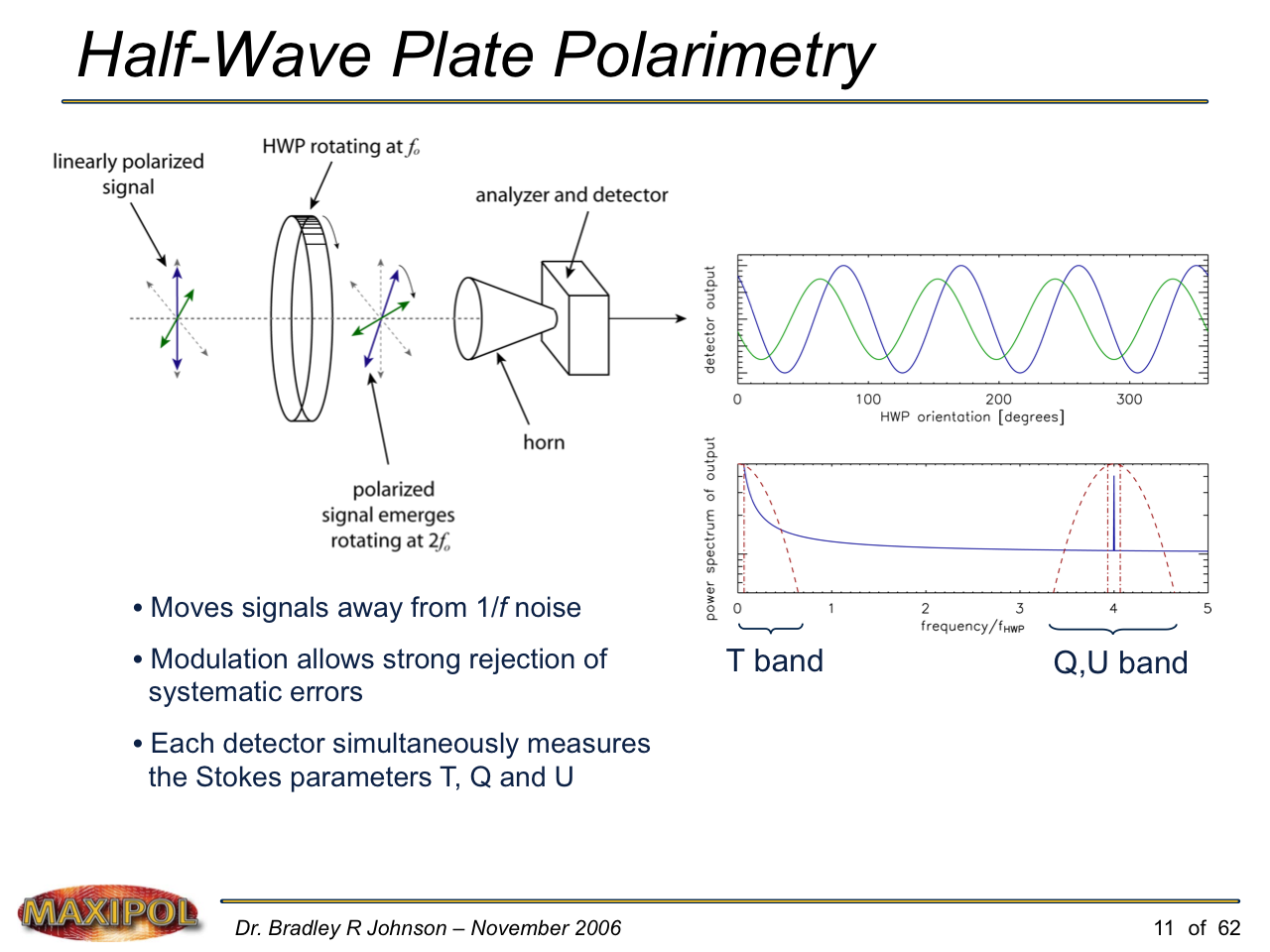
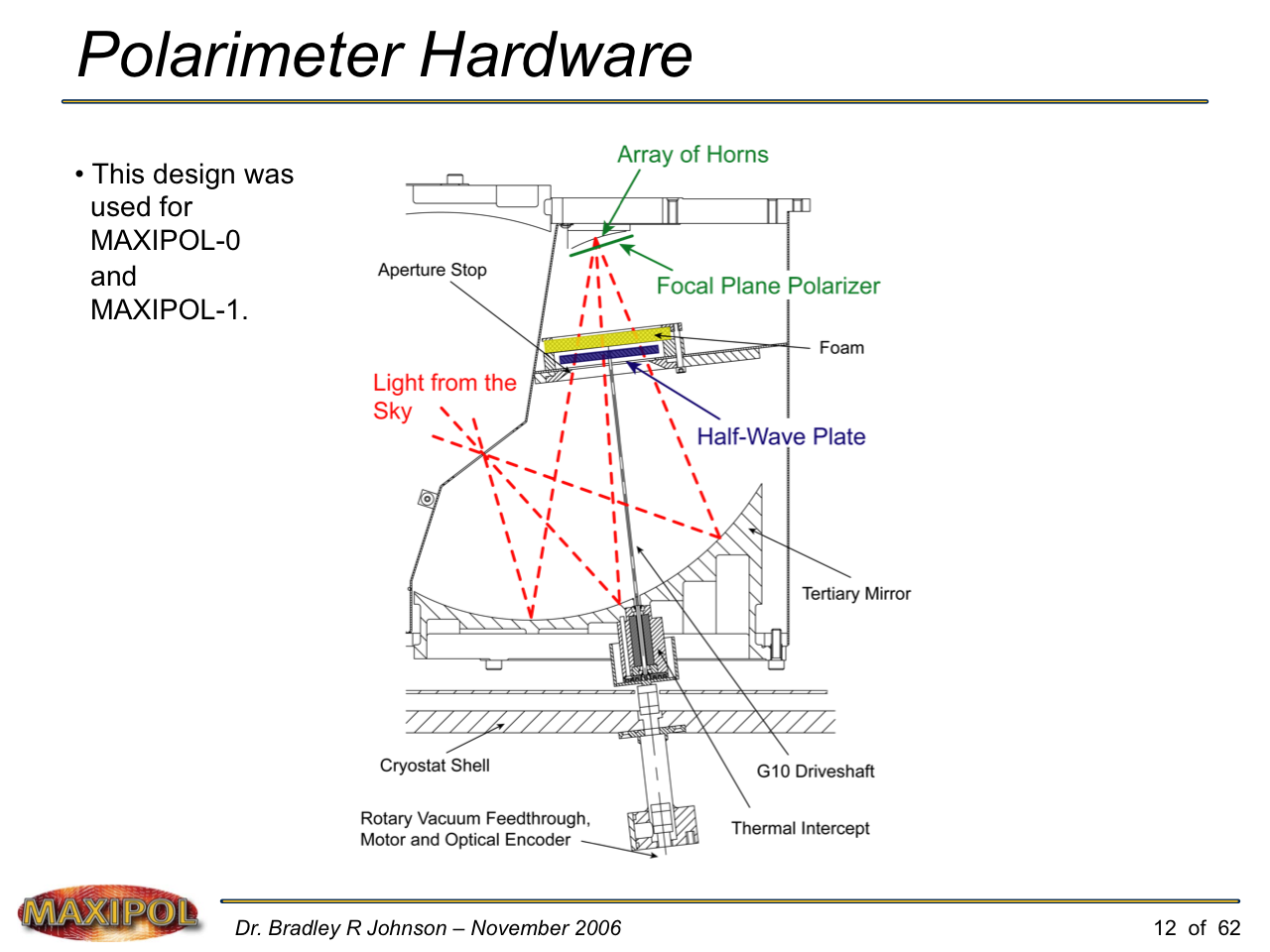
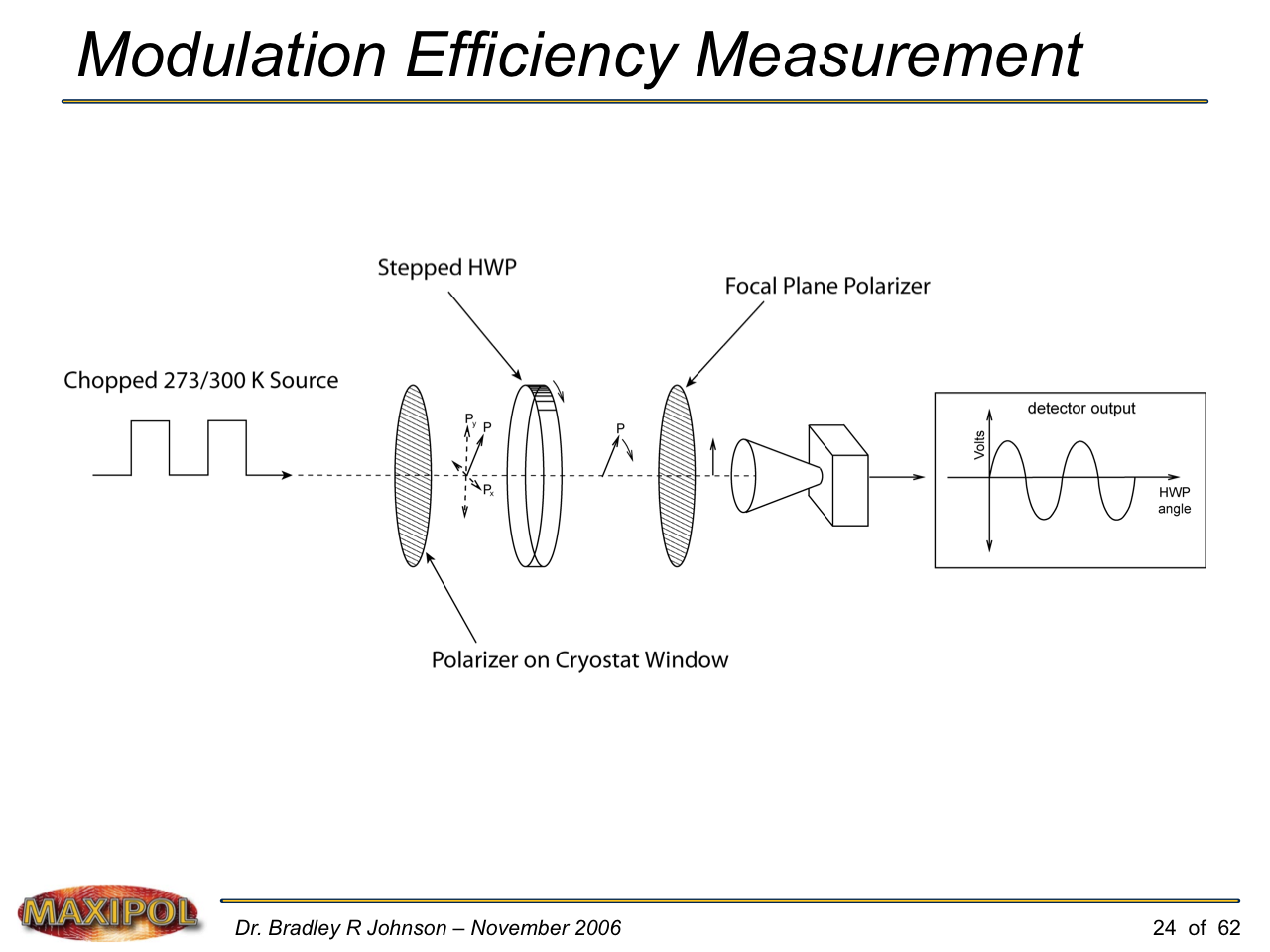
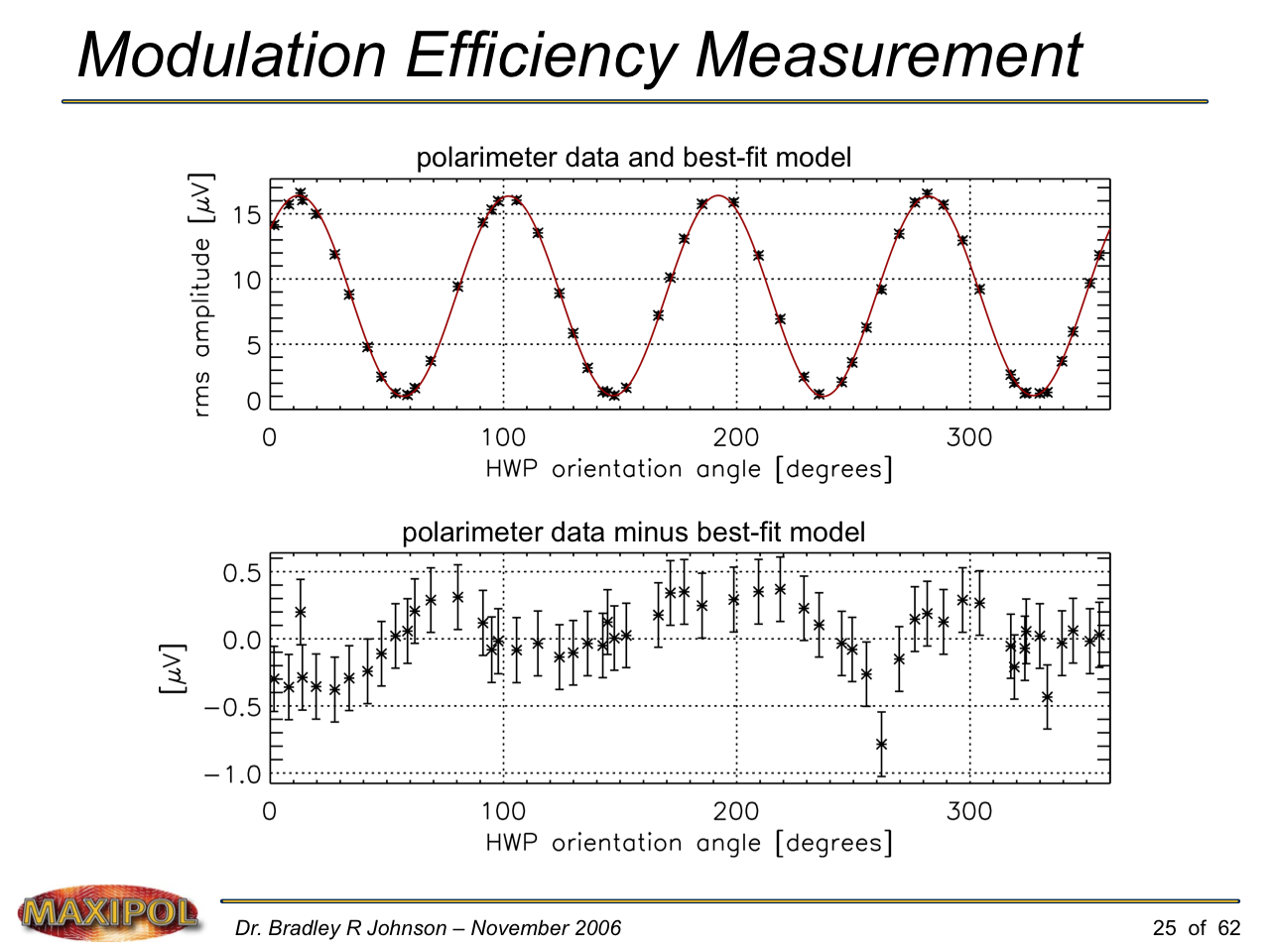
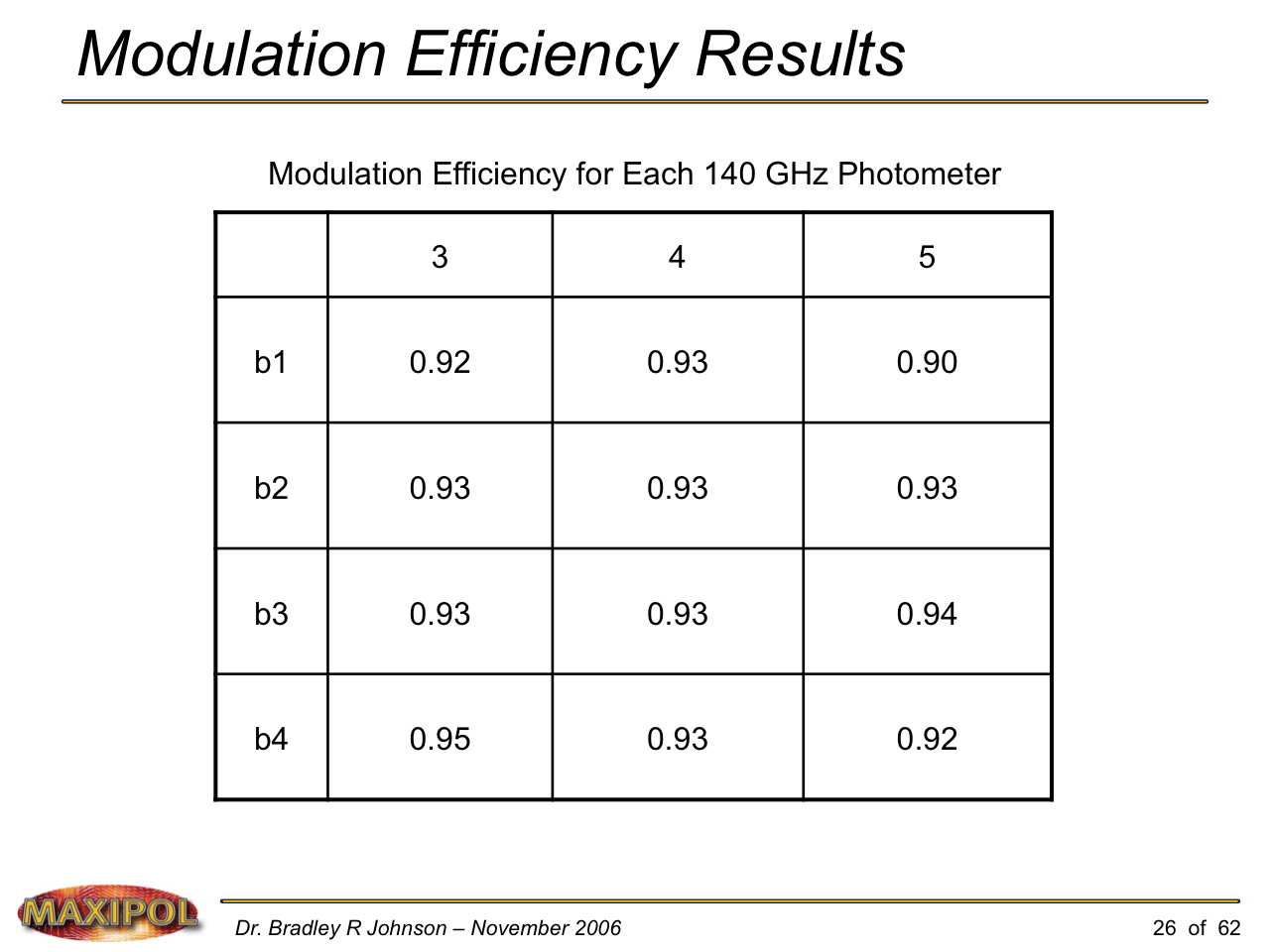
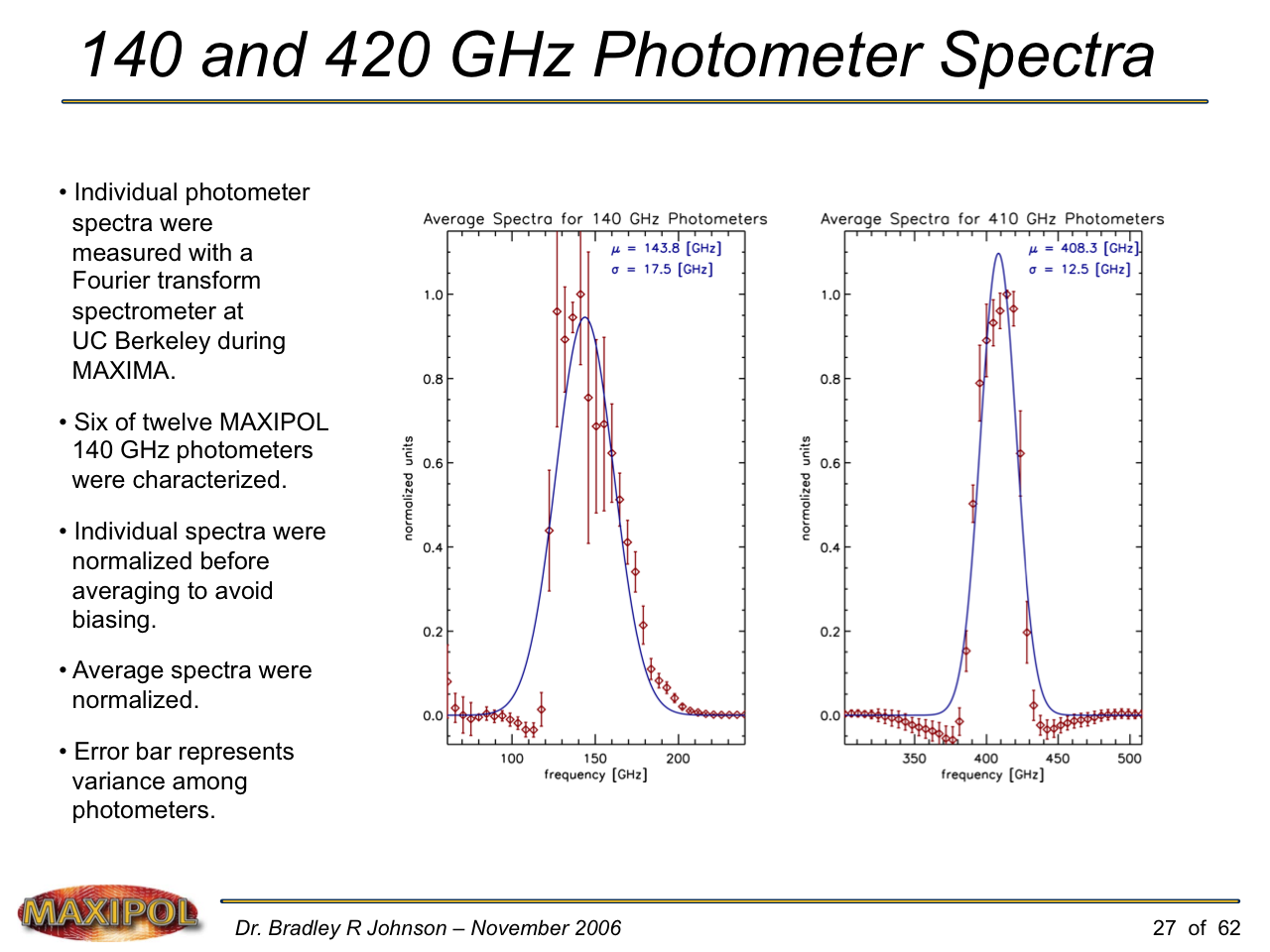
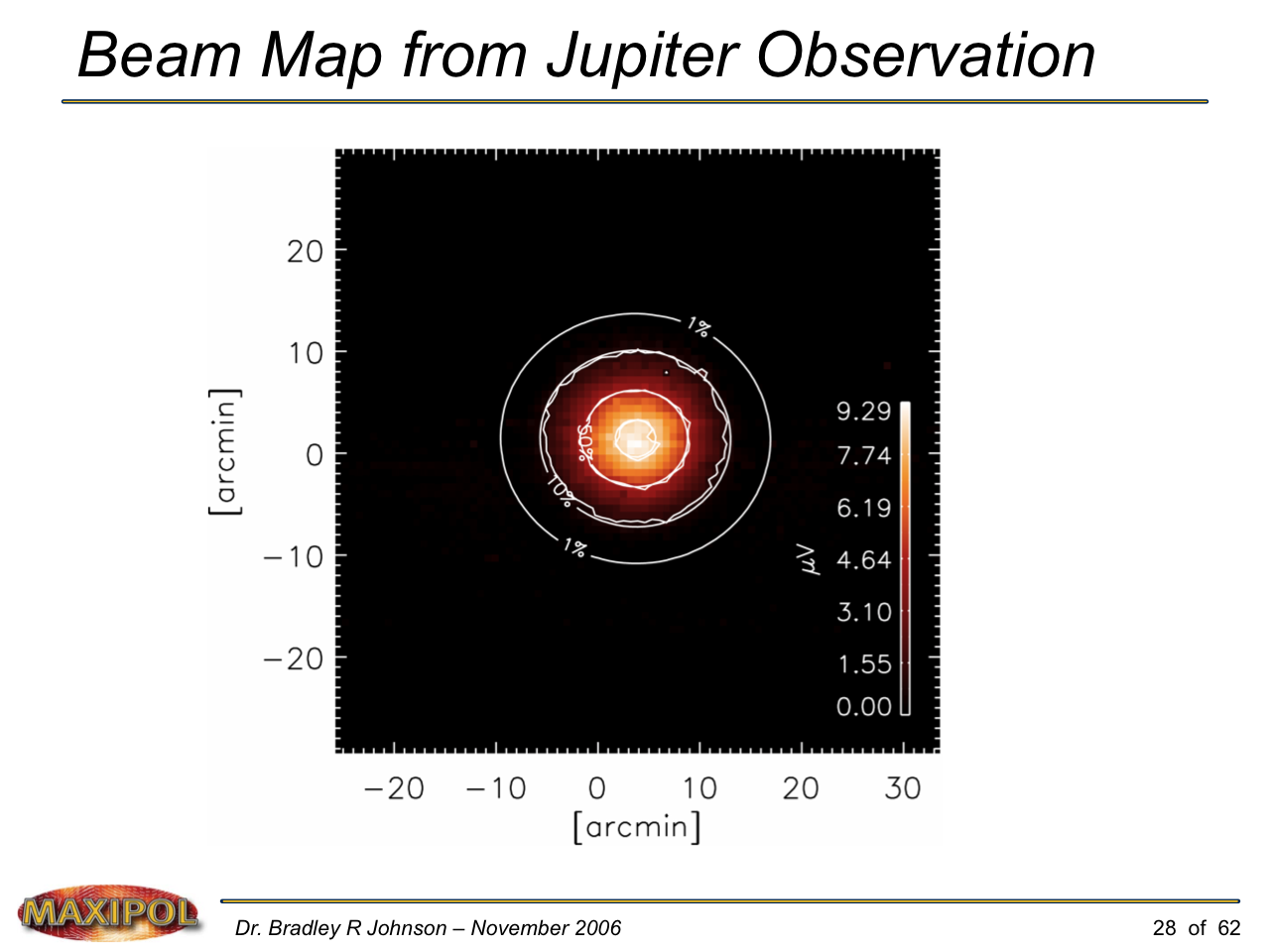
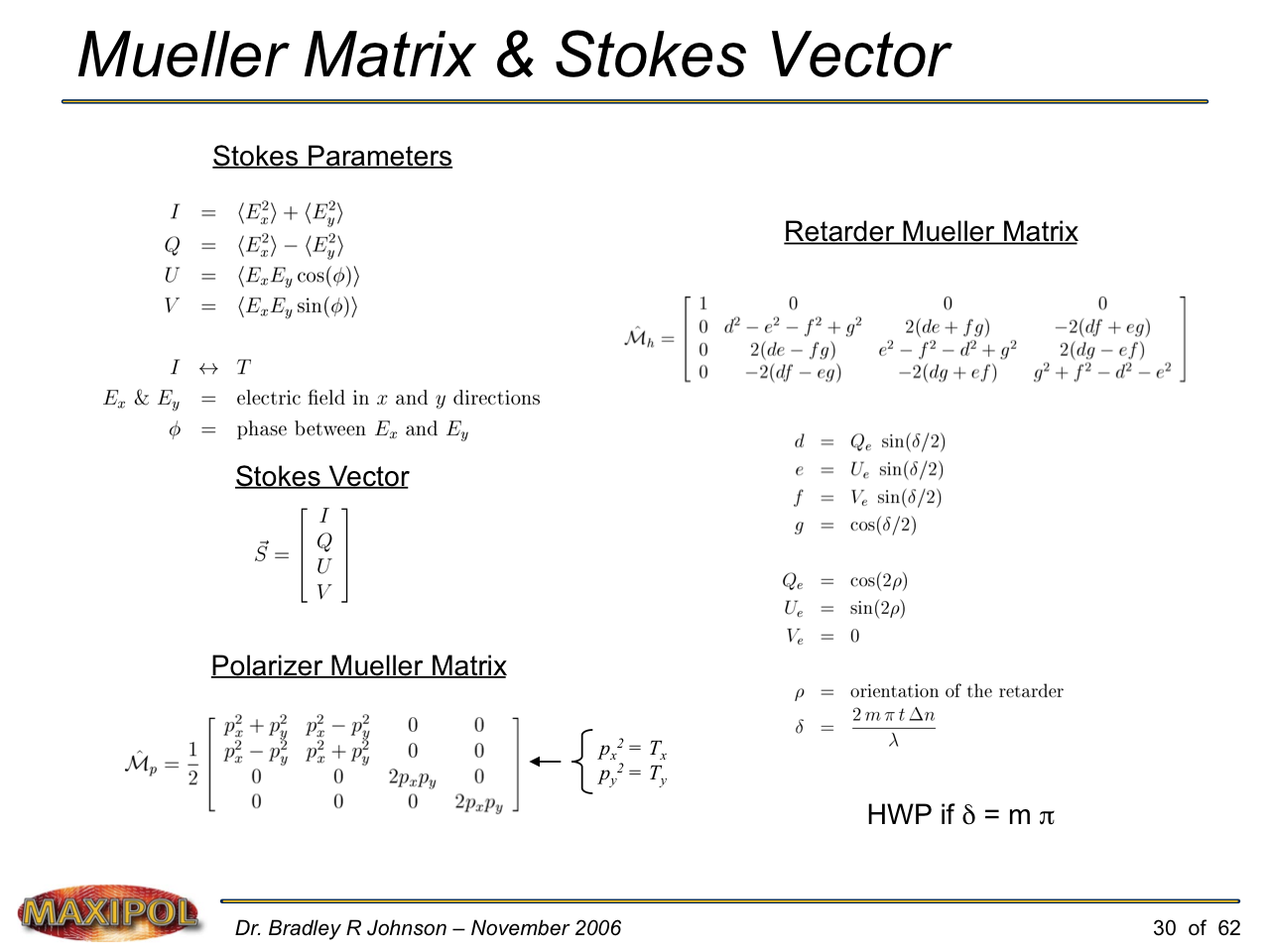
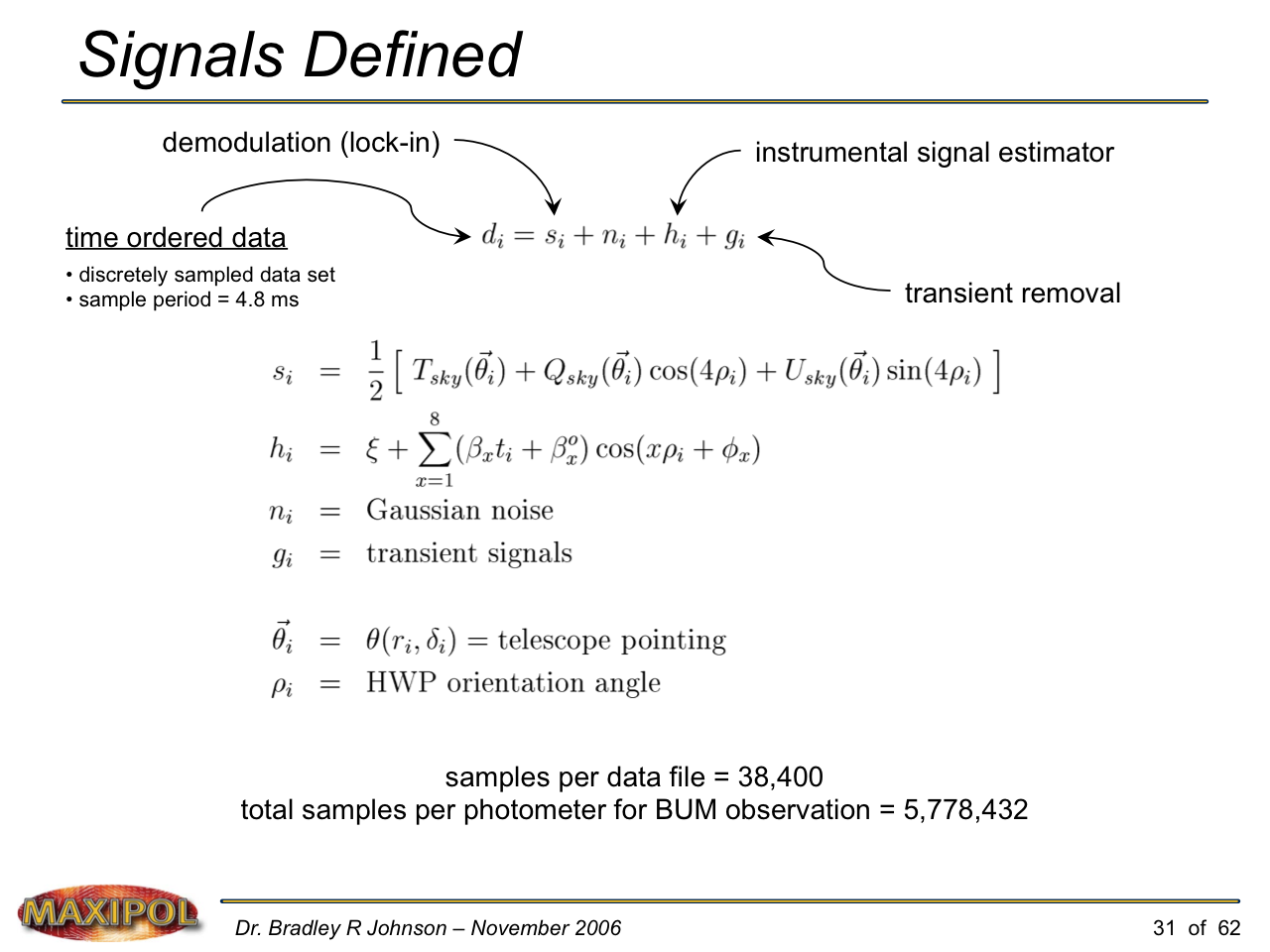
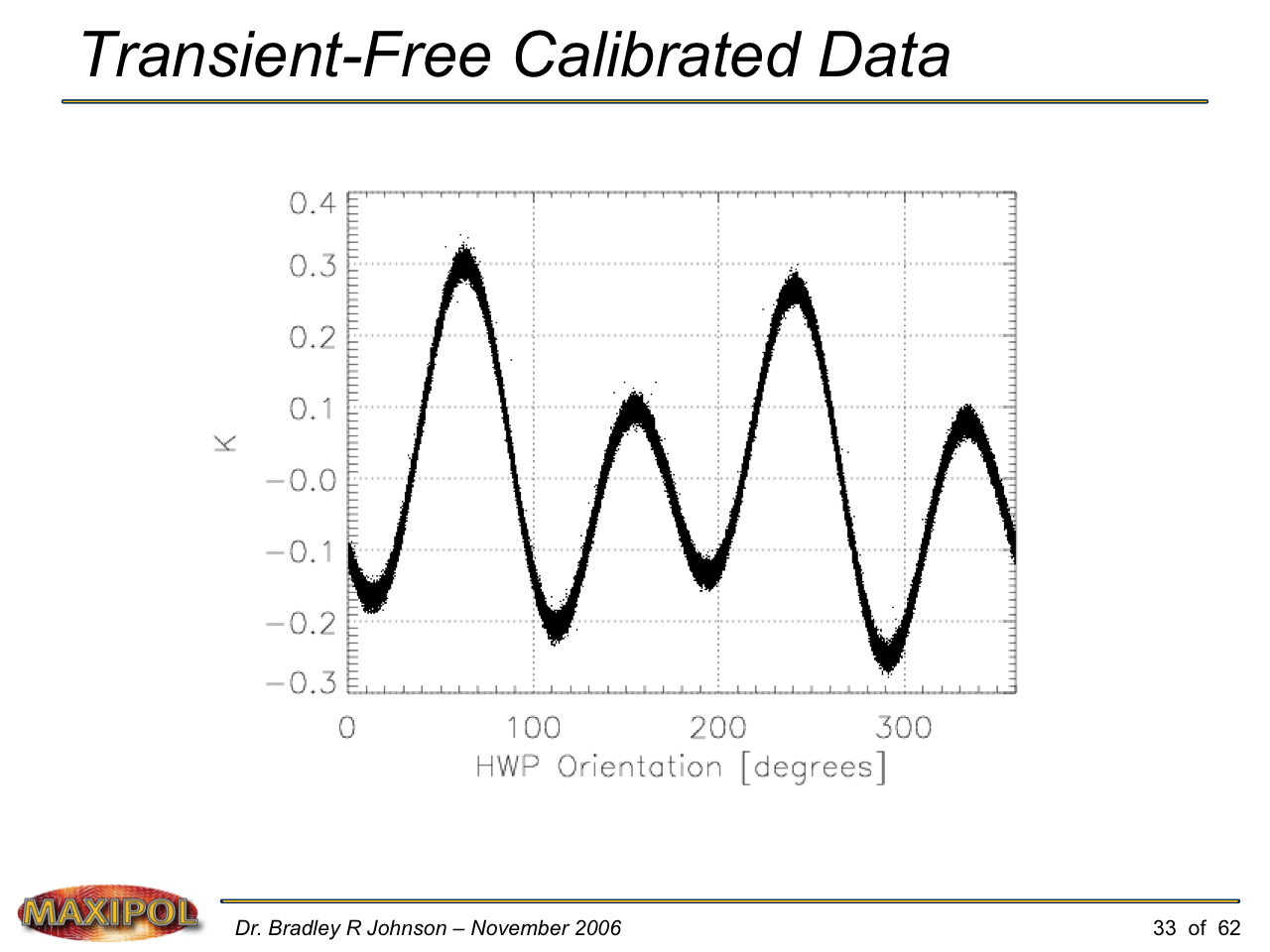
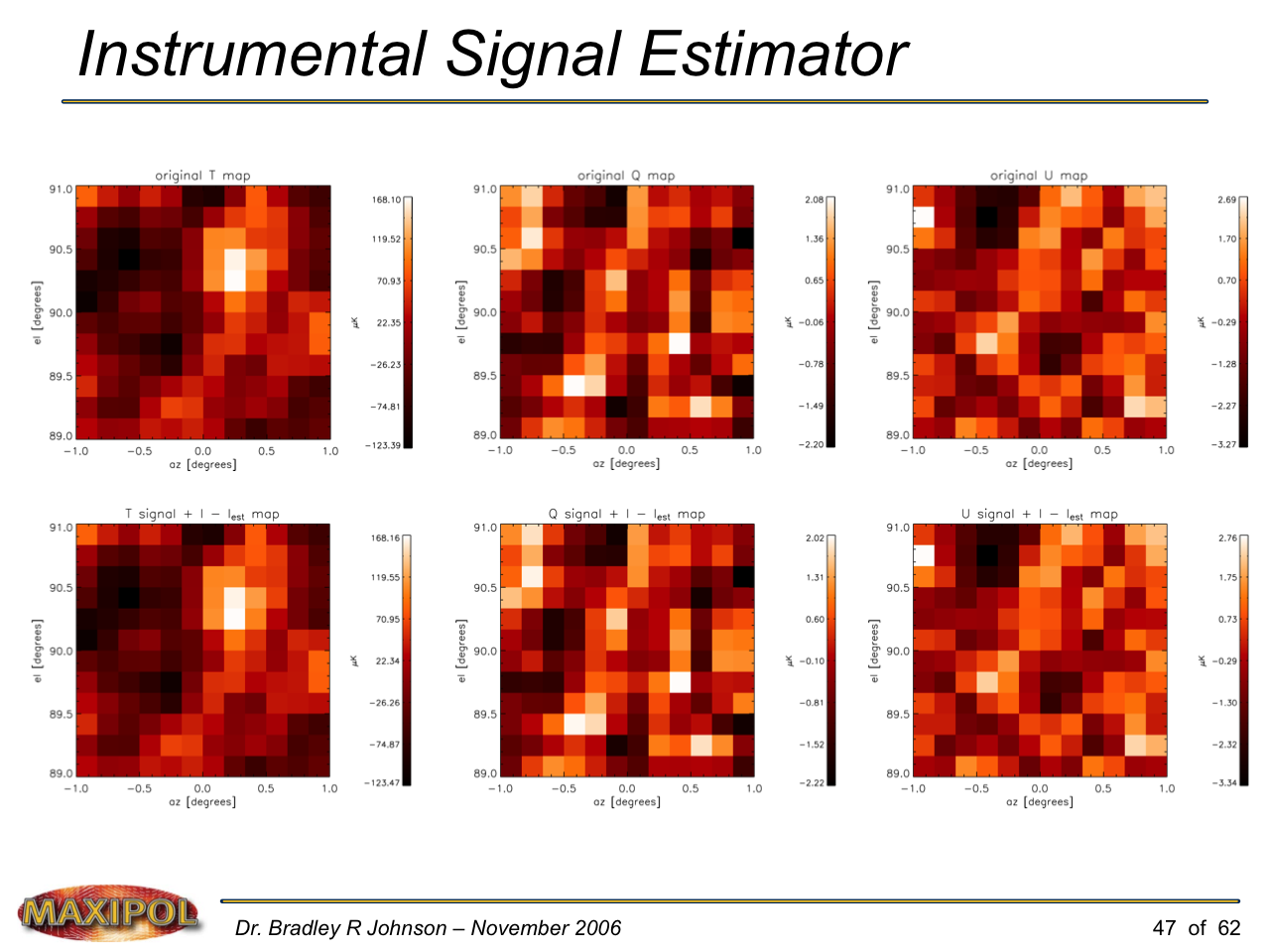
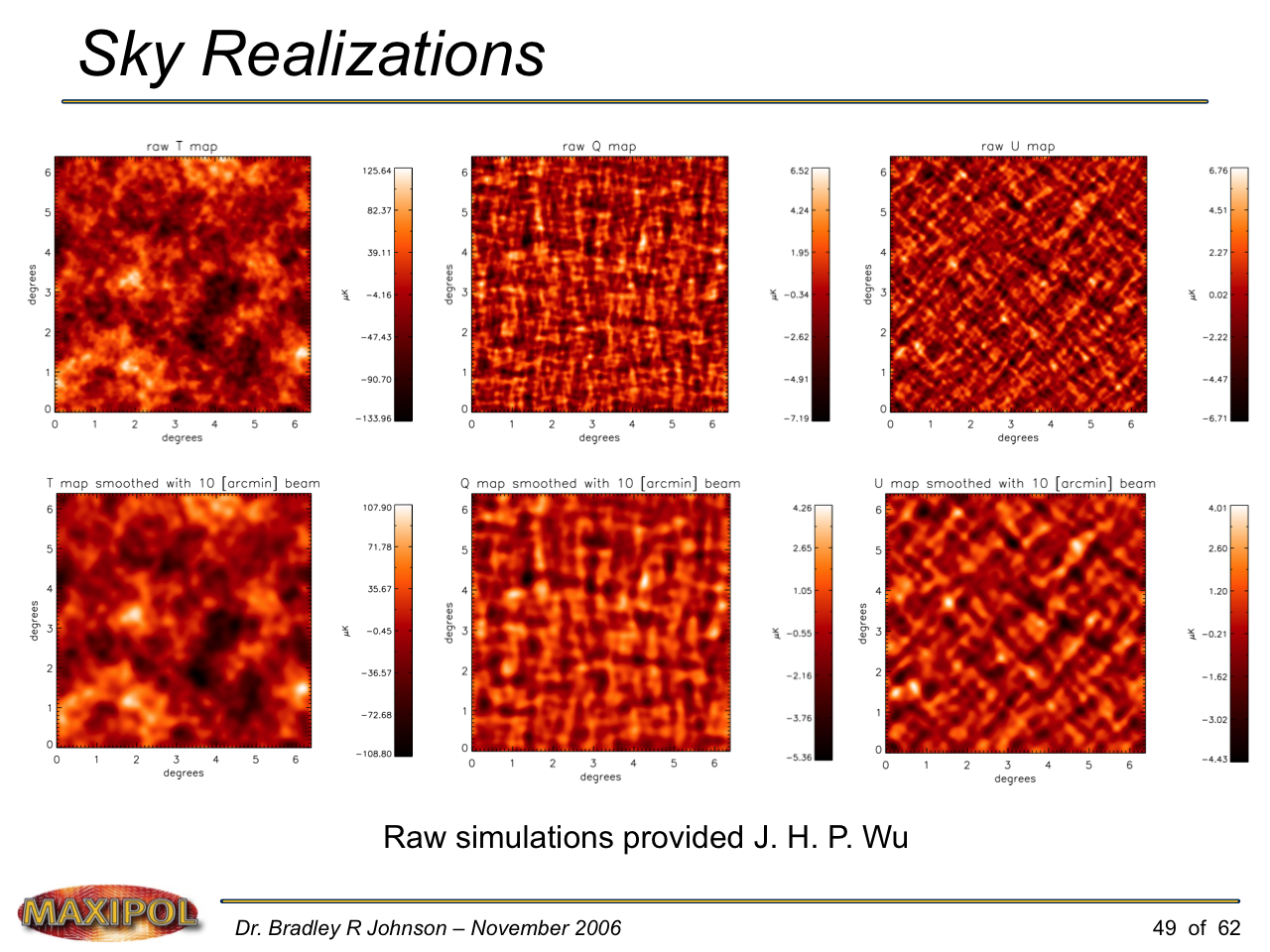
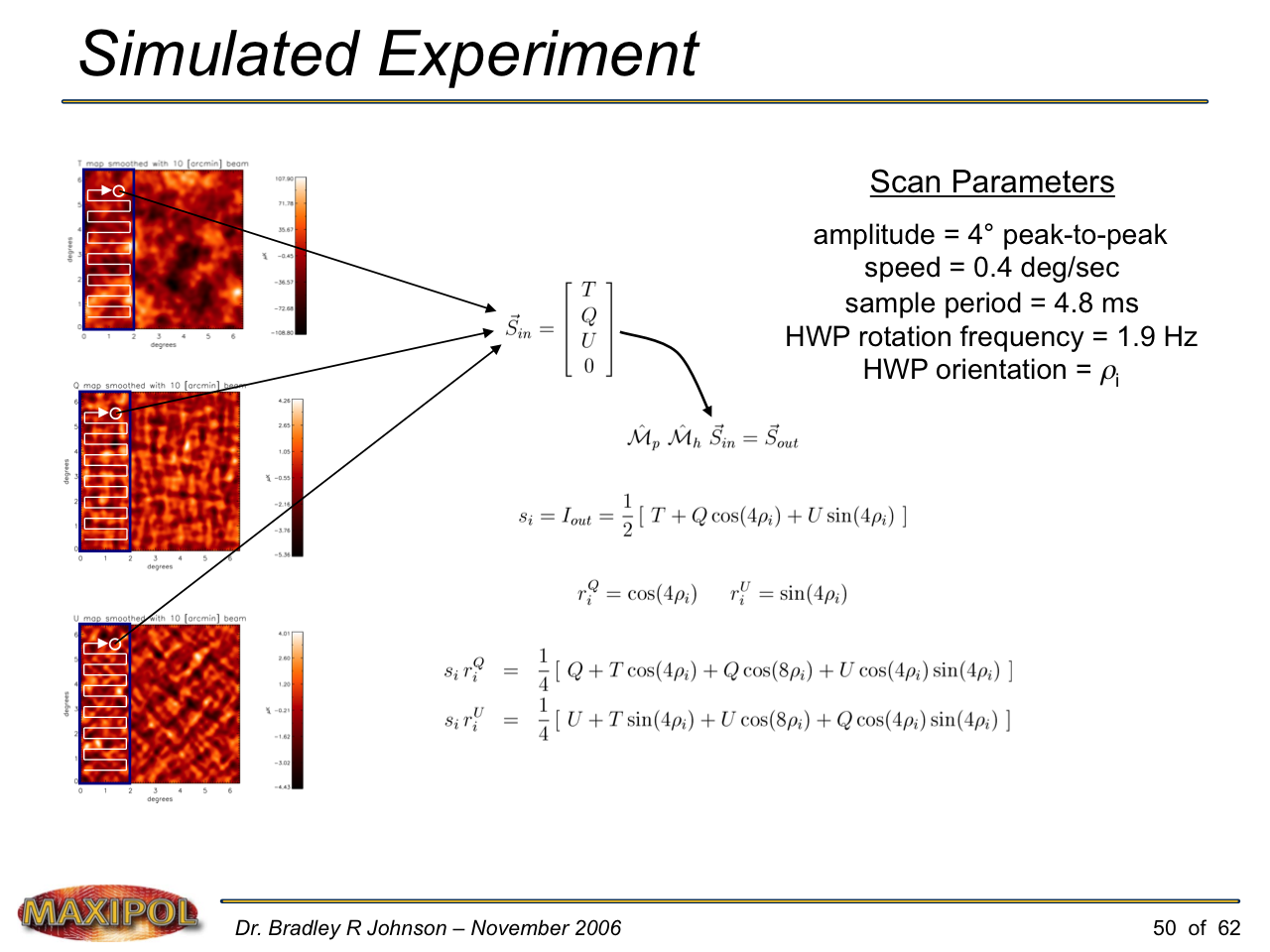
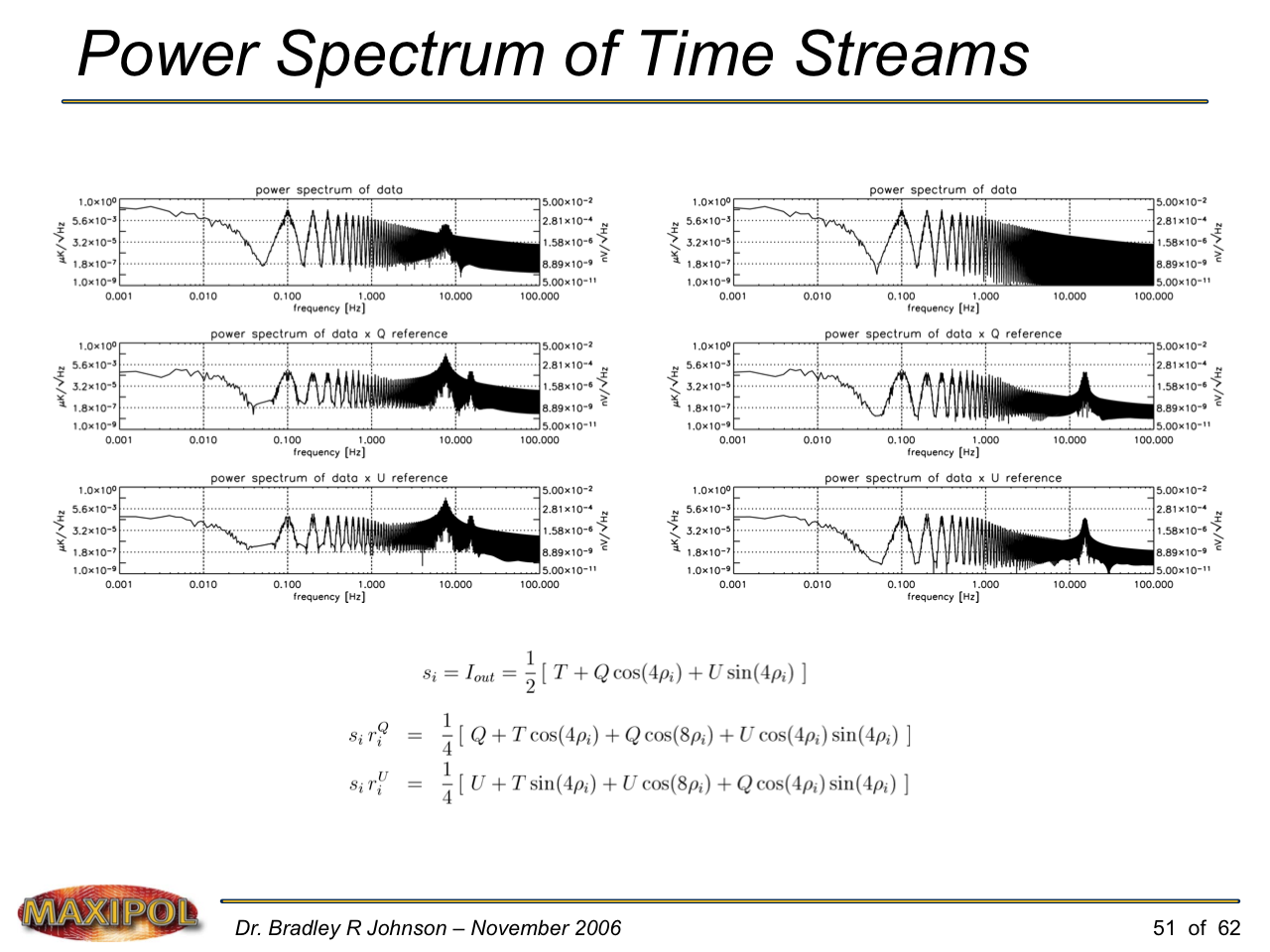
MAXIPOL (my Ph.D. thesis project) was a bolometric balloon-borne experiment designed to measure the E-mode polarization of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). MAXIPOL was the first bolometric CMB experiment to observe the sky using rapid polarization modulation. To build MAXIPOL, the CMB temperature anisotropy experiment MAXIMA was retrofitted with a rotating half-wave plate and a stationary analyzer. Observations were made with 12 polarimeters operating at 140 GHz with a FWHM beam size of 10′. MAXIPOL was launched twice (see videos below) and ultimately made a detection of the expected E-mode signal.






























































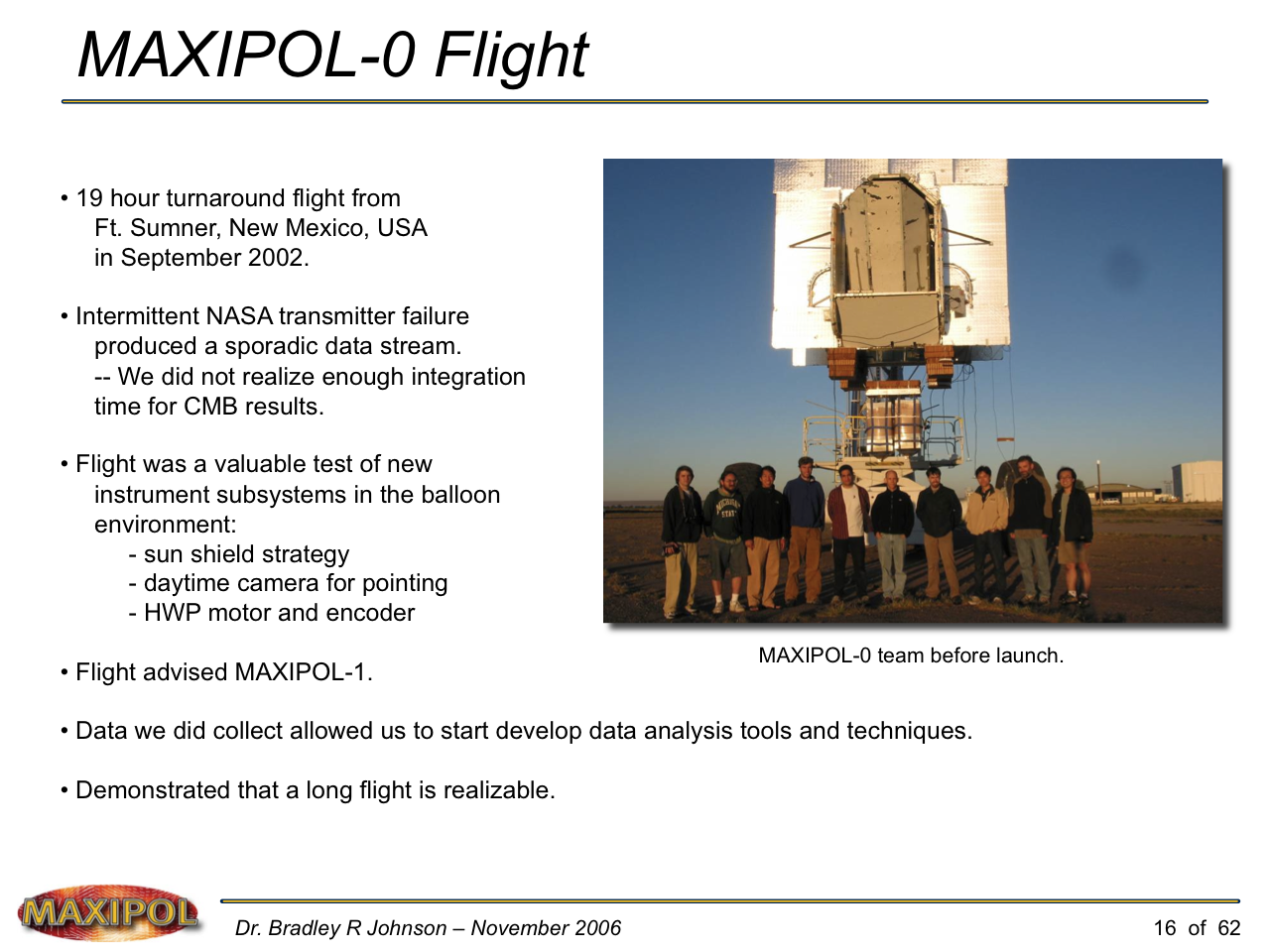
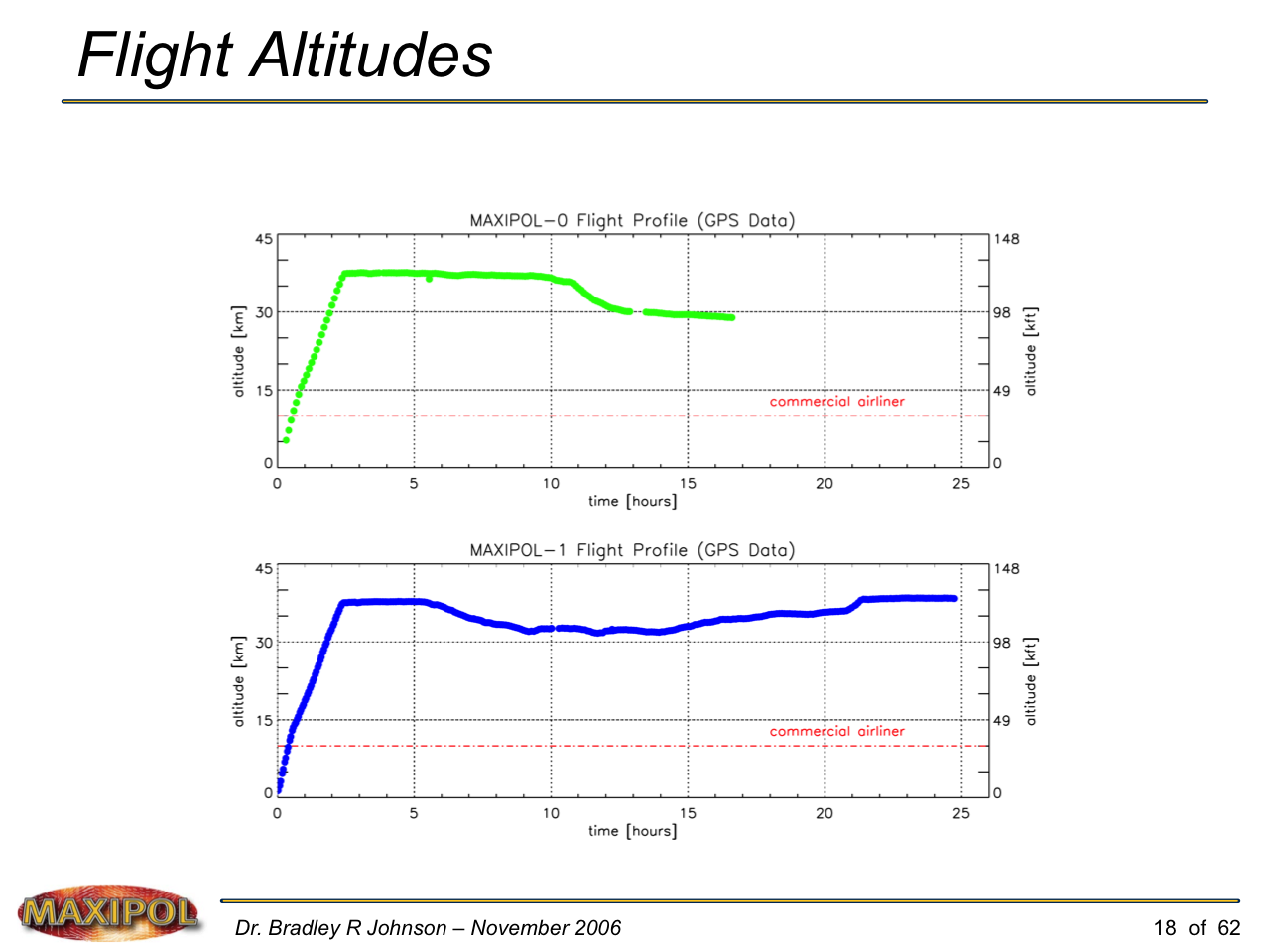
MAXIPOL-0 Launch from NASA’s Columbia Scientific Ballooning Facility in Ft. Sumner, New Mexico — September 2002.
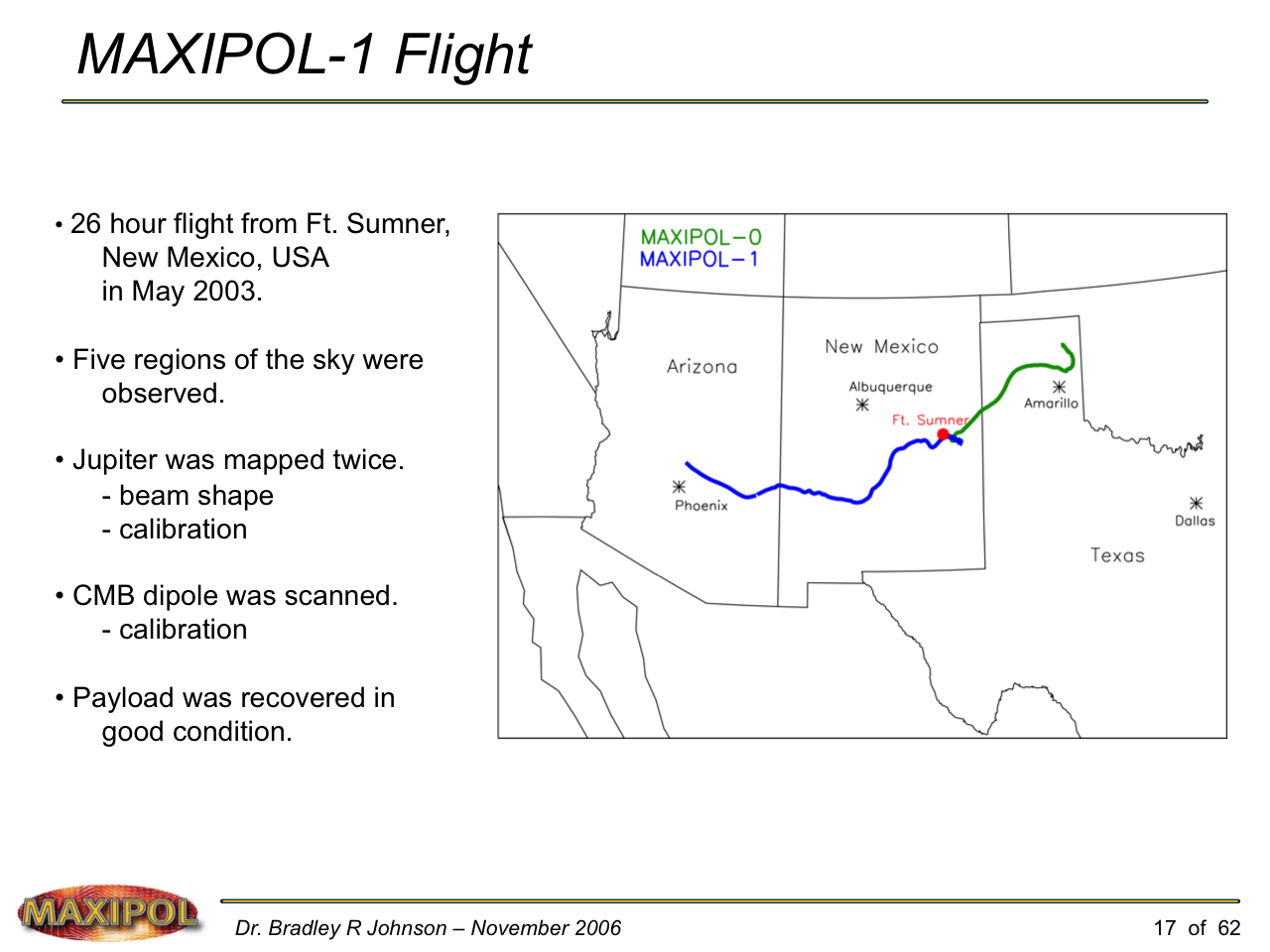
MAXIPOL-1 Launch from NASA’s Columbia Scientific Ballooning Facility in Ft. Sumner, New Mexico — May 2003.
“MAXIPOL: Data Analysis and Results.” Wu, J. H. P., et al. (2007) ApJ, 665, 55. (arXiv)
“Half-Wave Plate Polarimetry with MAXIPOL.” Johnson, B. R., et al. (2006) Proceedings of the XLIst Rencontres de Moriond, “Contents and Structures of the Universe.” LaThuile, Italy. March 18-25, 2006. edited by Christophe Magneville, Reza Ansari, Jacques Dumarchez and Jean Tran Thanh Van. The Gioi Publishers. VN-TG-7176-1 (27-9-2006).
“MAXIPOL: A Balloon-borne Experiment for Measuring the Polarization Anisotropy of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation.” Johnson, B. R., et al. (2003) New Astronomy Reviews, 47, 11-12, 1067. (arXiv)